Securing Web Apps on Kubernetes with TLS Using AWS Load Balancer Controller and Traefik
Introduction
- YouTube Tutorial
In our previous guide, we explored how to secure a Kubernetes web application using TLS with AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) and the default Kubernetes Service of type LoadBalancer. However, this approach didn’t use the AWS Load Balancer Controller.
While it worked, the default Kubernetes Service controller provisions:
-
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) for HTTP/HTTPS (now deprecated)
-
Network Load Balancer (NLB) for TCP/UDP
Although NLBs are suitable for specific use cases, Application Load Balancers (ALBs) offer advanced features such as path-based and host-based routing—making them ideal for modern web applications.
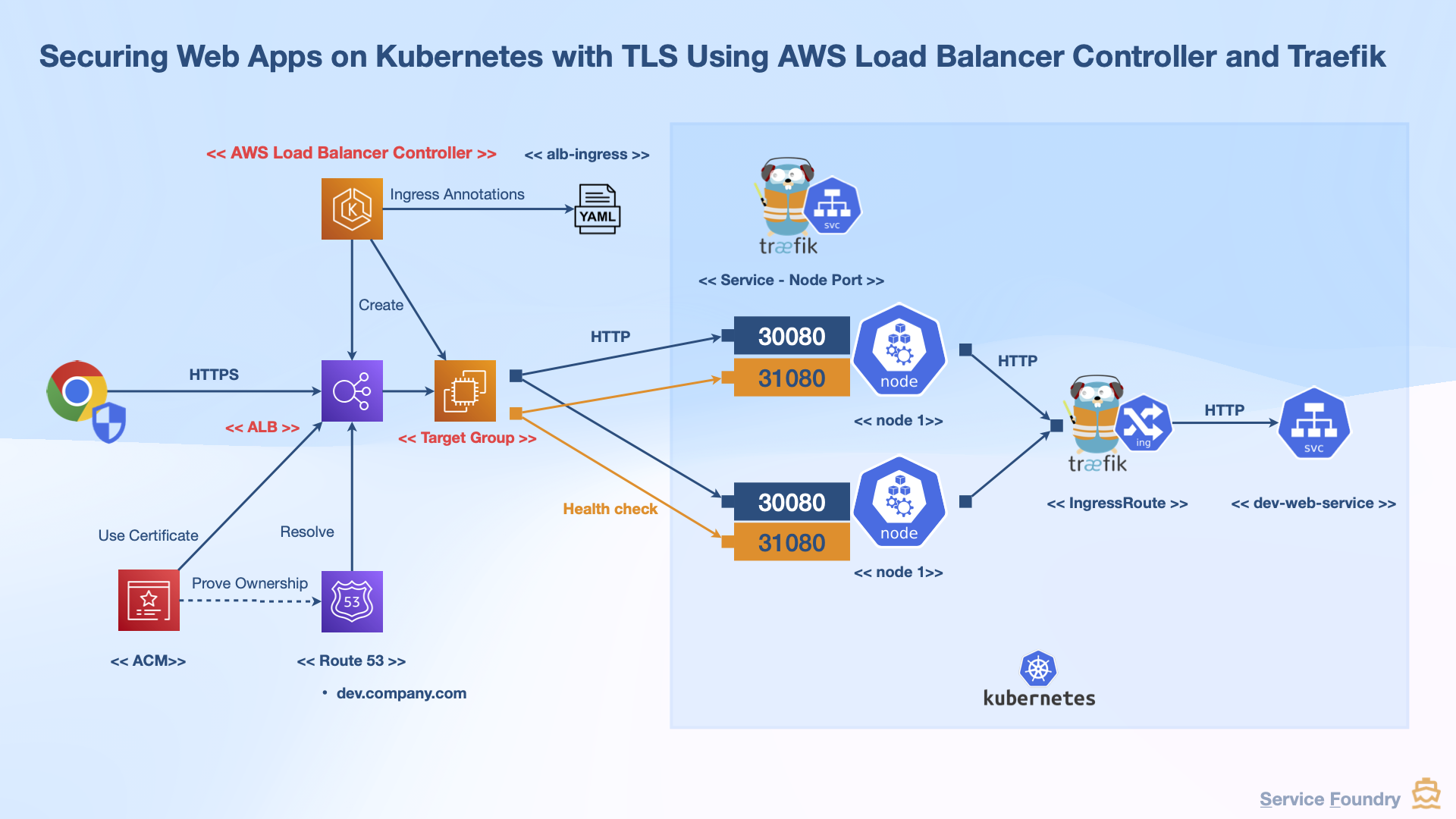
This guide walks you through installing and configuring the AWS Load Balancer Controller to provision an ALB for your Kubernetes workloads. We’ll also demonstrate how to integrate Traefik as your Ingress Controller with this setup.
What Is the AWS Load Balancer Controller?
The AWS Load Balancer Controller helps manage AWS Elastic Load Balancers for Kubernetes workloads. It automatically creates and manages ALBs or NLBs based on your Kubernetes Ingress or Service resources.
This lets you expose your applications through a single DNS endpoint managed by AWS.
Step-by-Step Setup Overview
-
Install the AWS Load Balancer Controller
-
Install the Traefik Ingress Controller using NodePort
-
Configure an ALB Ingress resource for Traefik
-
Update Route 53 DNS records
-
Test HTTPS access to your app
Installing the AWS Load Balancer Controller
We’ll use Helm to install the controller. First, add and update the EKS Helm chart repository:
$ helm repo add eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
$ helm repo update eksThen save the default configuration for version 1.14.1:
$ helm pull eks/aws-load-balancer-controller
$ helm show values eks/aws-load-balancer-controller > values-1.14.1.yamlCreate IAM Role Using eksctl
We need a service account with appropriate IAM permissions:
$ eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--cluster=$EKS_CLUSTER_NAME \
--namespace=kube-system \
--name=aws-load-balancer-controller \
--attach-policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/ElasticLoadBalancingFullAccess \
--attach-policy-arn=arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:policy/AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy \
--override-existing-serviceaccounts \
--region $AWS_REGION \
--approveVerify the service account exists:
$ kubectl get serviceaccount -n kube-system aws-load-balancer-controller -o yamlTroubleshooting
When you have already installed the controller before, you might fail to create iamserviceaccount.
You need to delete the CloudFormation stack created by the controller first.
If you tried to delete it using the eksctl, it will fail.
$ eksctl delete iamserviceaccount --cluster $EKS_CLUSTER_NAME --region $AWS_REGION --namespace kube-system --name aws-load-balancer-controller
# Example output
2025-12-26 20:49:01 [ℹ] 1 iamserviceaccount (kube-system/aws-load-balancer-controller) was included (based on the include/exclude rules)
2025-12-26 20:49:03 [ℹ] 1 task: {
2 sequential sub-tasks: {
delete IAM role for serviceaccount "kube-system/aws-load-balancer-controller" [async],
delete serviceaccount "kube-system/aws-load-balancer-controller",
} }2025-12-26 20:49:03 [ℹ] 1 error(s) occurred and IAM Role stacks haven't been deleted properly, you may wish to check CloudFormation console
2025-12-26 20:49:03 [✖] not able to delete stack "eksctl-nsa2-sf-addon-iamserviceaccount-kube-system-aws-load-balancer-controller": operation error CloudFormation: DeleteStack, https response error StatusCode: 400, RequestID: 9b2143dd-4bf5-43b5-9dad-79f99e747620, api error ValidationError: Stack [arn:aws:cloudformation:ca-central-1:445567090745:stack/eksctl-nsa2-sf-addon-iamserviceaccount-kube-system-aws-load-balancer-controller/a1d74f30-e287-11f0-ba9a-029ad0288513] cannot be deleted while TerminationProtection is enabled
Error: failed to delete iamserviceaccount(s)
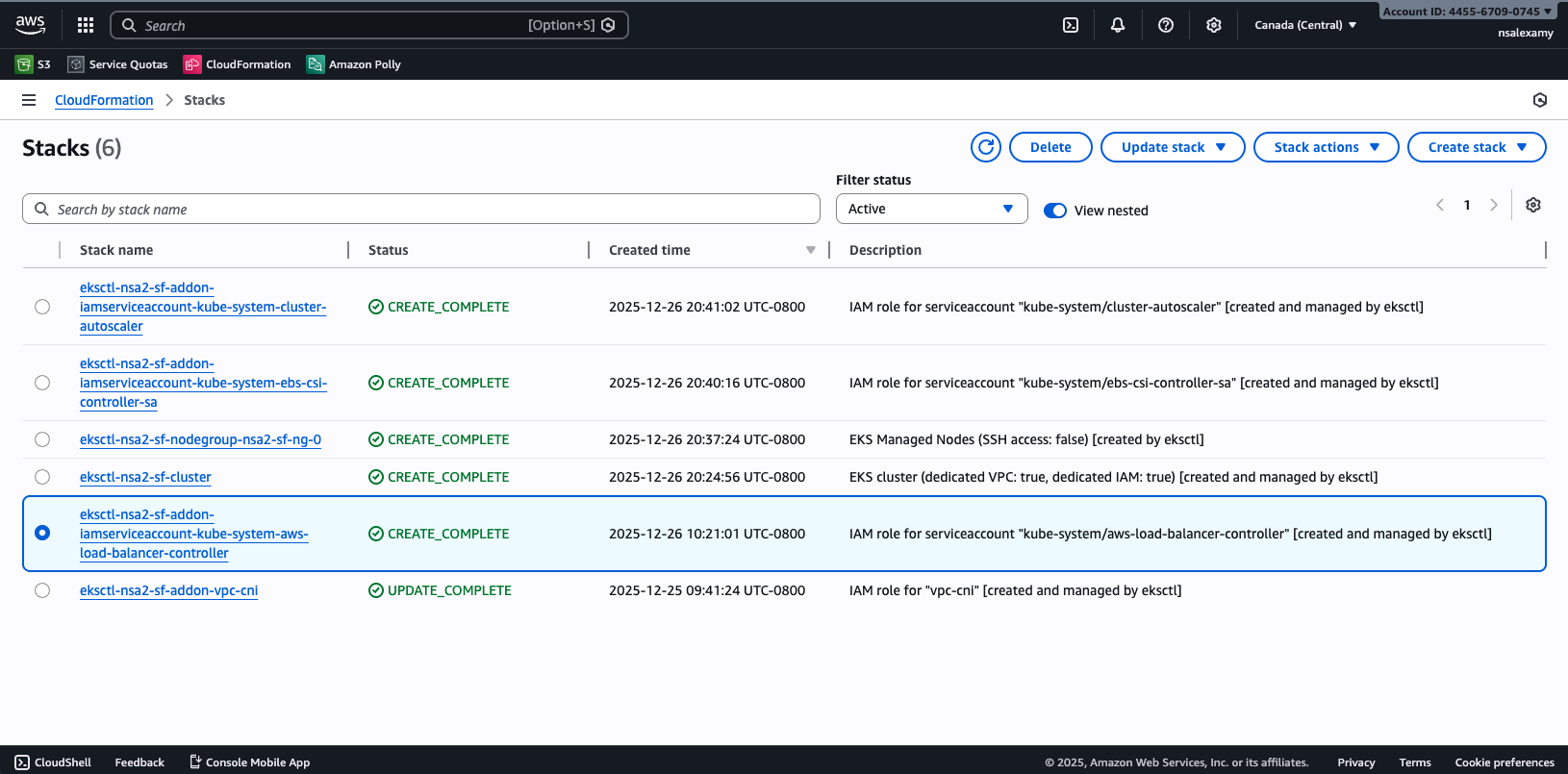
Select aws-load-balancer-controller stack and click on Delete button. And then click on Edit termination protection.
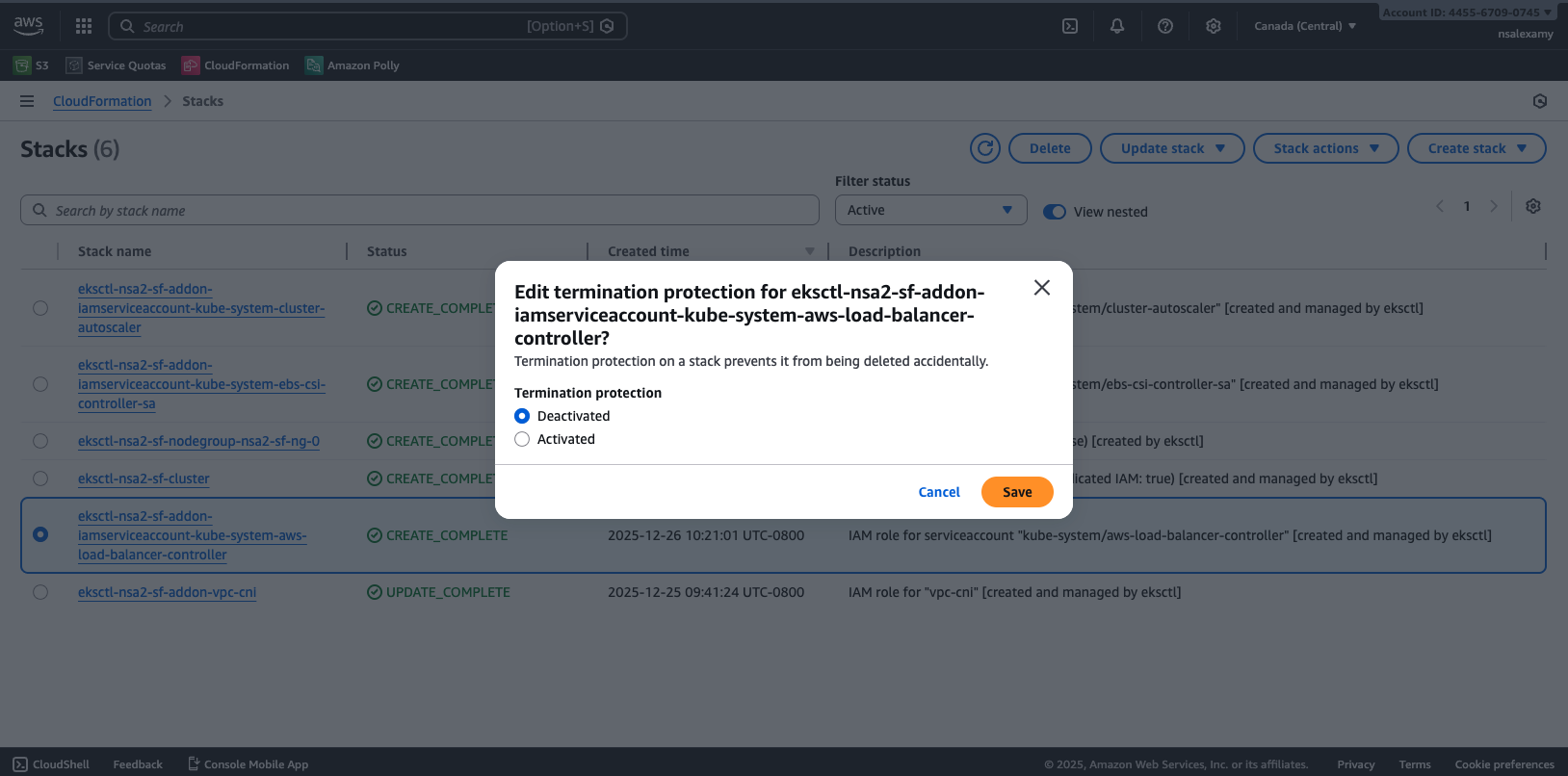
Select Termination protection Deactivated and click on Delete stack button.
Configure Helm Custom Values
Use these settings in your custom values file:
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: aws-load-balancer-controller
clusterName: your-eks-cluster-nameInstall the controller:
$ helm install aws-load-balancer-controller eks/aws-load-balancer-controller \
-f k8s/aws-load-balancer-controller/custom-values.yaml \
--namespace kube-system --create-namespace --version 1.14.1Confirm that the controller is running:
$ kubectl get deployment -n kube-system aws-load-balancer-controllerInstalling Traefik with NodePort for ALB
To route traffic through an ALB, Traefik must expose its service as NodePort:
ingressRoute:
healthcheck:
enabled: true
ports:
traefik:
nodePort: 31080
expose:
default: true
web:
port: 80
nodePort: 30080
websecure:
port: 443
nodePort: 30443
service:
type: NodePortInstall Traefik:
$ helm upgrade --install traefik traefik/traefik \
-f k8s/alb-traefik/custom-values.yaml \
--namespace traefik --create-namespaceCreating the ALB Ingress Resource
Define an Ingress with the right annotations to instruct the controller to create an ALB:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: traefik-alb
namespace: traefik
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-name: traefik-alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/tags: "servicefoundry.org/service-name=traefik/traefik-alb,servicefoundry.org/provider=service-foundry"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: instance
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /ping
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: '31080'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:aws-region:aws-account-id:certificate/certificate-arn
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- host: '*.servicefoundry.org'
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: traefik
port:
number: 80Apply the Ingress:
$ kubectl apply -f k8s/alb-traefik/traefik-alb-ingress.yamlVerifying the ALB Setup
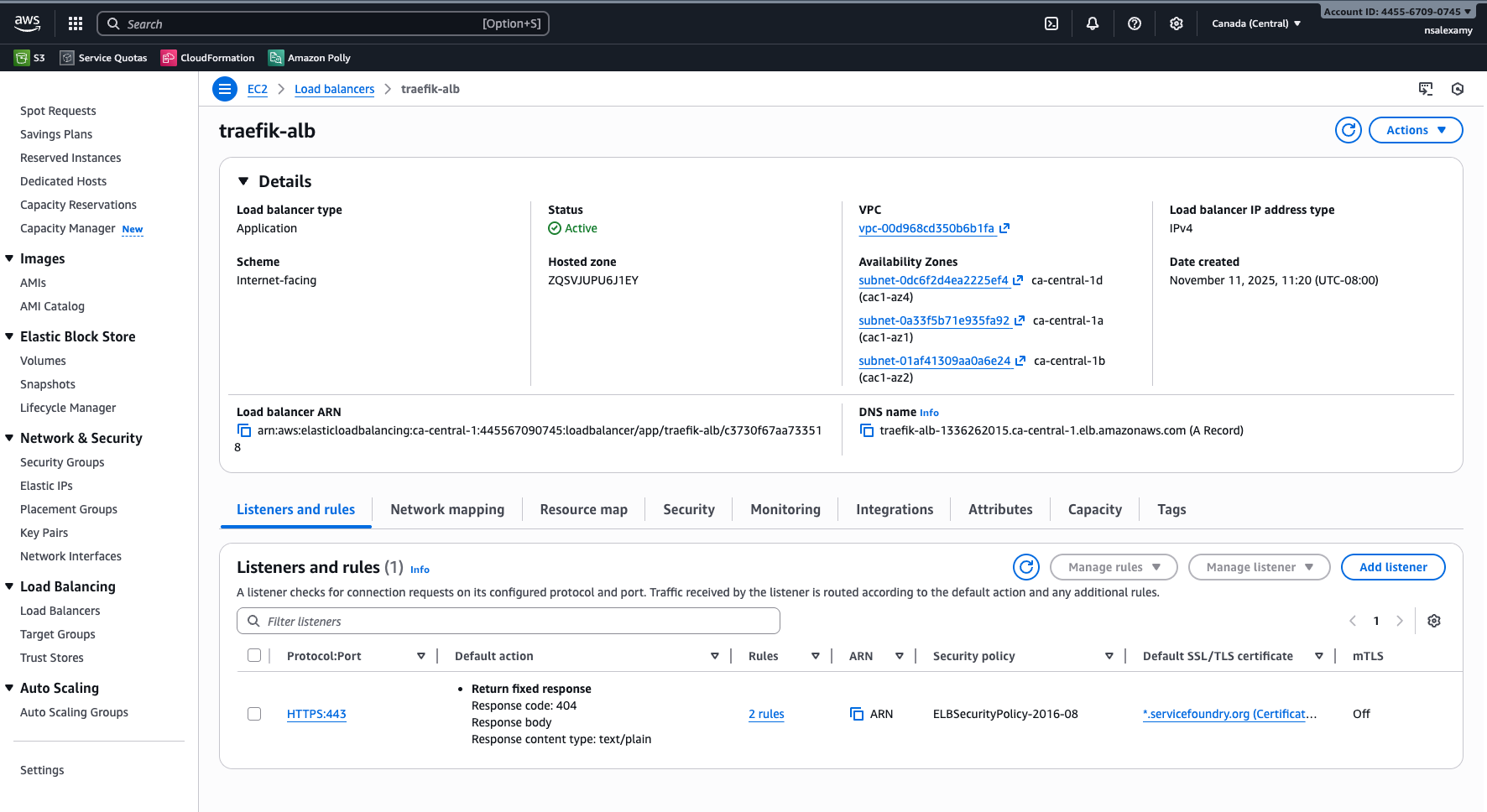
The ALB named traefik-alb is now created.
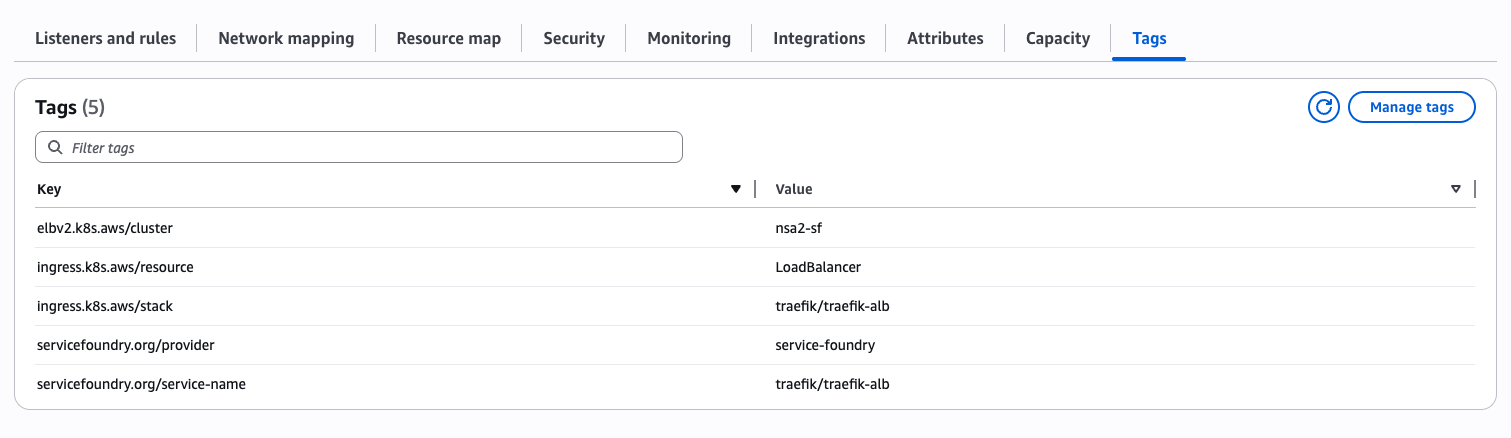
Tags added in the annotations appear in the Load Balancer’s AWS console and can be used by Terraform later.
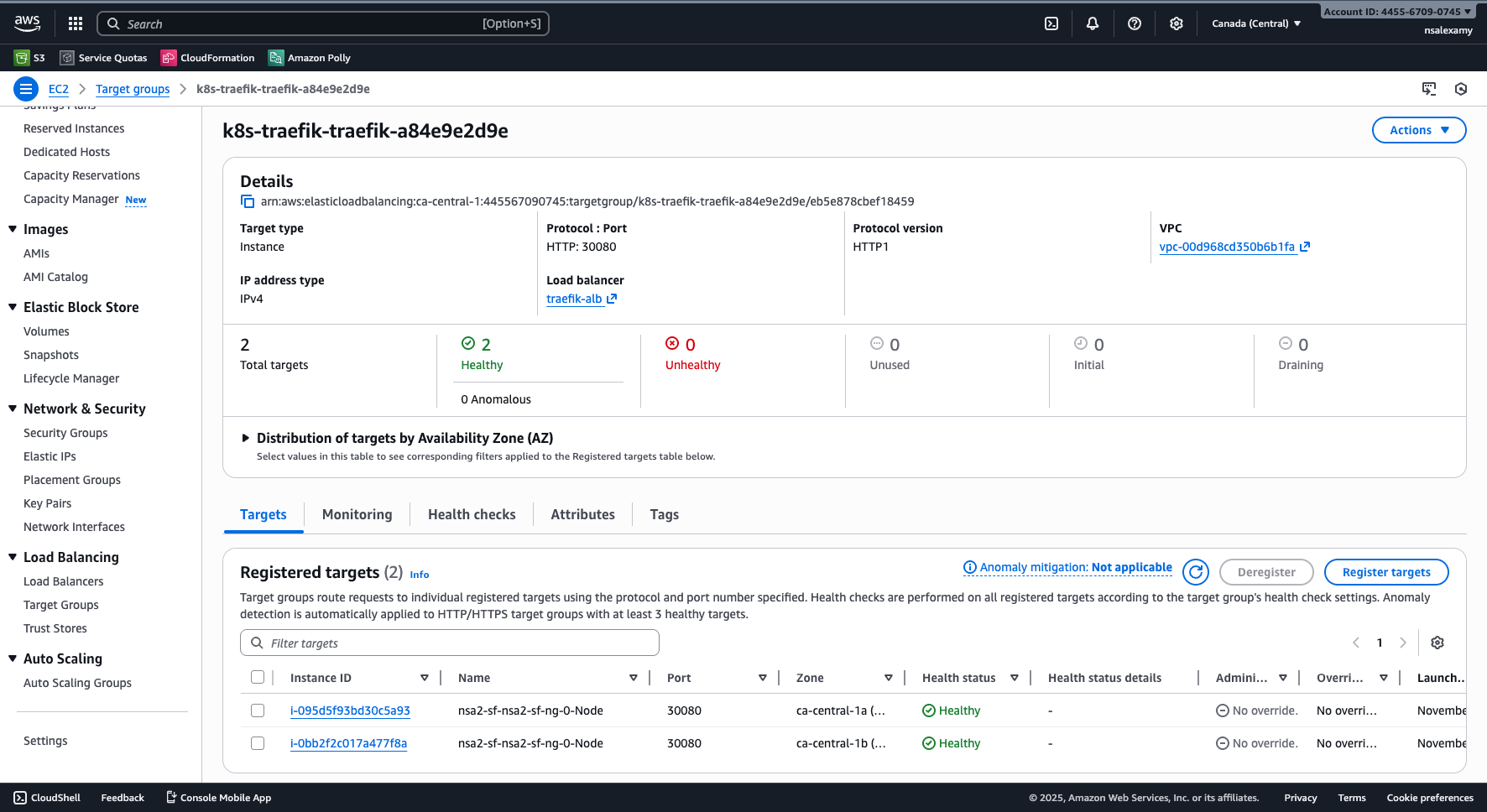
A target group is created automatically and linked to EC2 instances on port 30080.
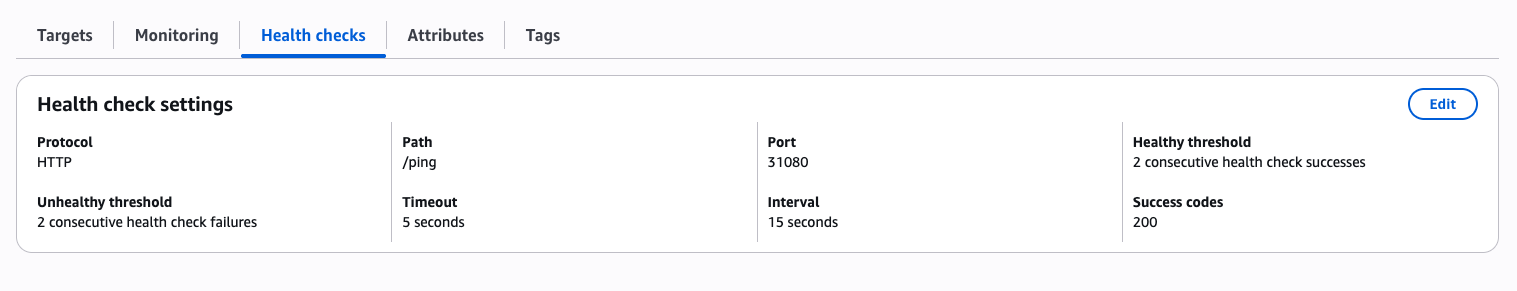
Health checks use the /ping path and port 31080 as defined in the annotations.
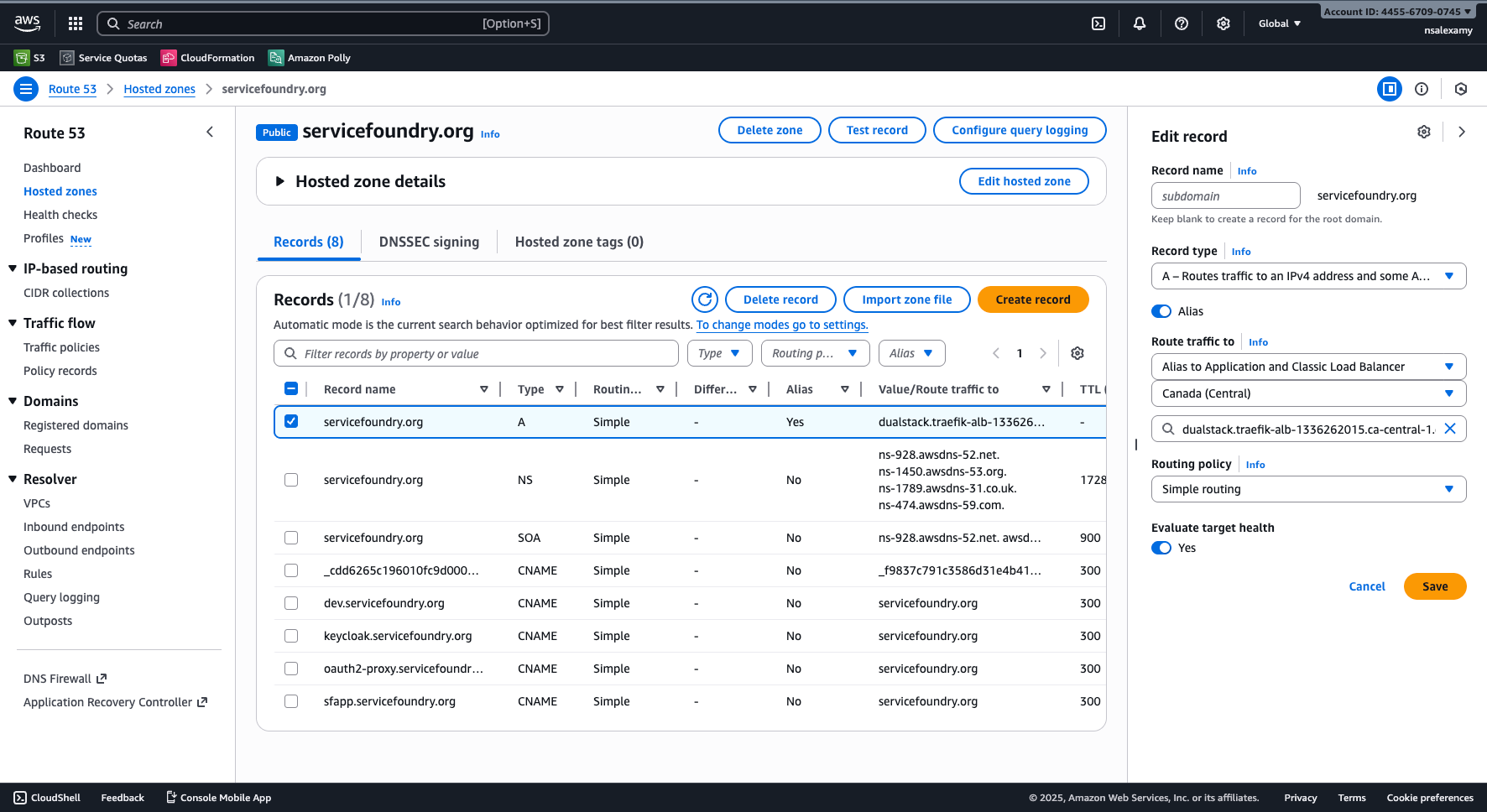
Updating DNS Records
Use Route 53 to map your domain (e.g., dev.servicefoundry.org) to the Load Balancer DNS name using Alias routing.
- TIP
-
In the next guide, we’ll show how to automate this using Terraform and tags.
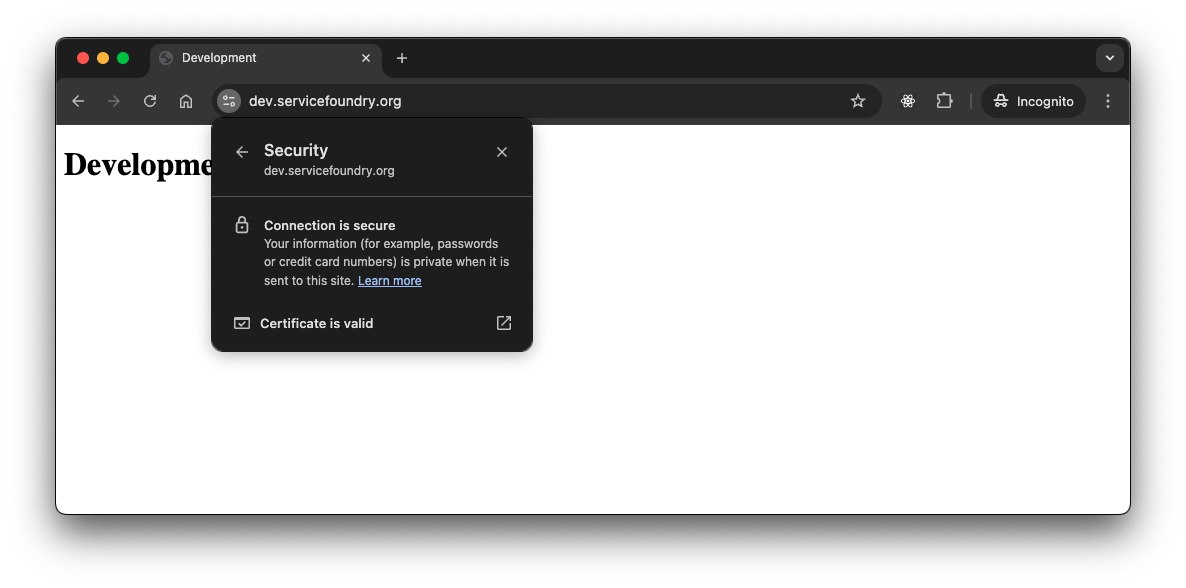
Verifying HTTPS Access
Once DNS is updated, navigate to https://dev.servicefoundry.org to verify your app is accessible over HTTPS.
Conclusion

We’ve successfully integrated the AWS Load Balancer Controller with Traefik to create an ALB that routes HTTPS traffic to our Kubernetes web application. This solution is more flexible and production-ready compared to using NLBs or CLBs, and it aligns with modern cloud-native architecture practices.
📘 View the web version: